sample menu
Gastroparesis refers to a delay in emptying stomach contents. Symptoms often include feeling full after eating a meal, or even a small amount of food, as well as nausea, vomiting, bloating or abdominal pain. The causes of gastroparesis may include diabetes mellitus, complications after surgery, kidney disease, certain medications, thyroid disorders, cancer, among others.
The following tips are intended to reduce symptoms and help maintain adequate nutrition.
|
Mealtime
|
||
|
Foods
|
|
|
Fluids
- Stay hydrated. Most adults need 6-10 cups of water per day. Sip slowly throughout the day.
- Drink fluids with meals, however; be sure not to fill up on liquids
- Avoid carbonated beverages as they can cause bloating
Otro
- Avoid alcohol as it can affect stomach emptying
- Foods that are acidic, spicy, or contain caffeine or mint may increase acid reflux
- Keep blood sugars under control if you have diabetes
- Keep a food diary to track your intake and find foods that are best tolerated
- Exercise may increase stomach emptying and reduce symptoms. Walking after meals is suggested.
See below for help in choosing more optimal foods from each food group:
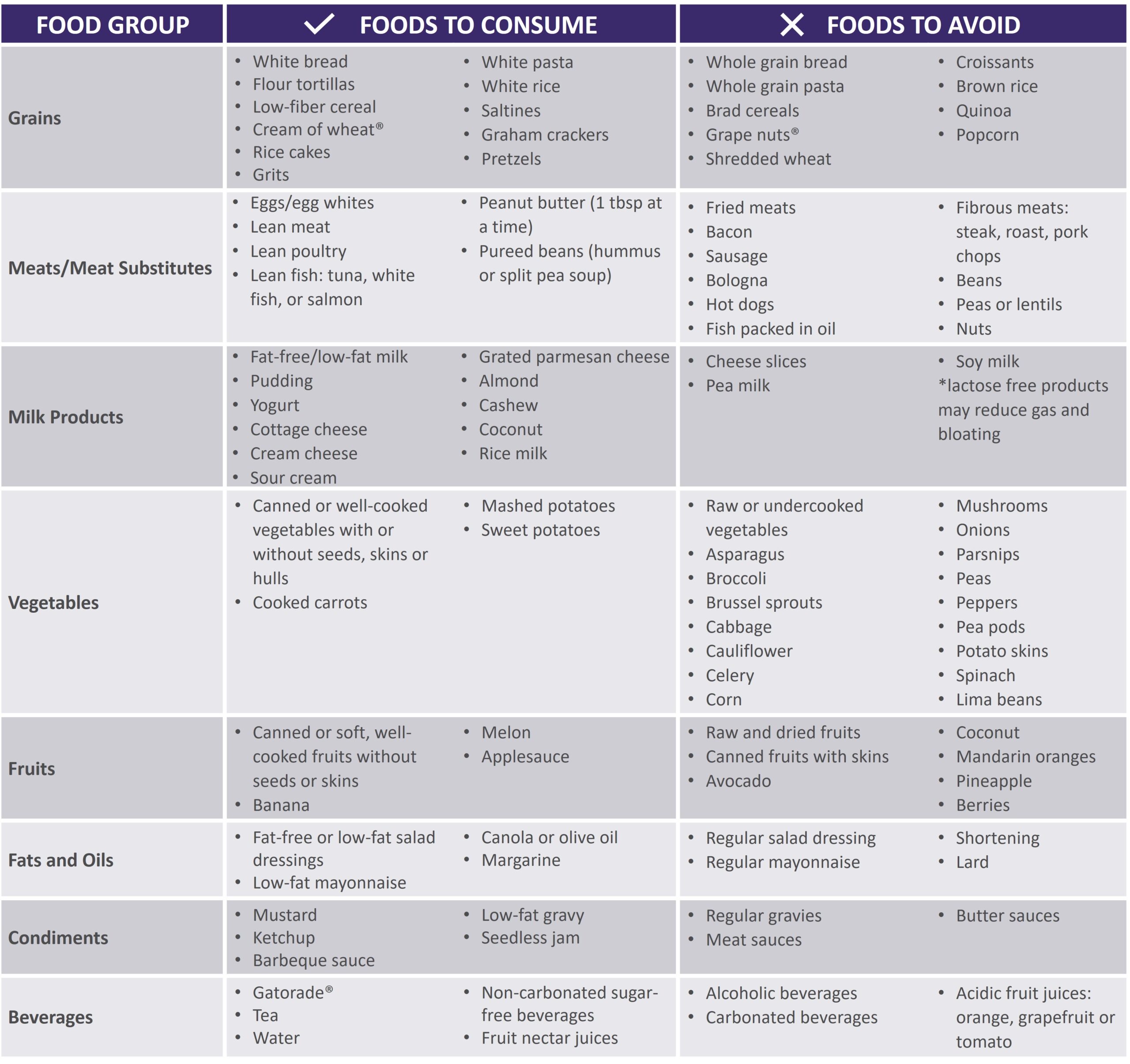 |
|
Gastroparesis Sample Menus |
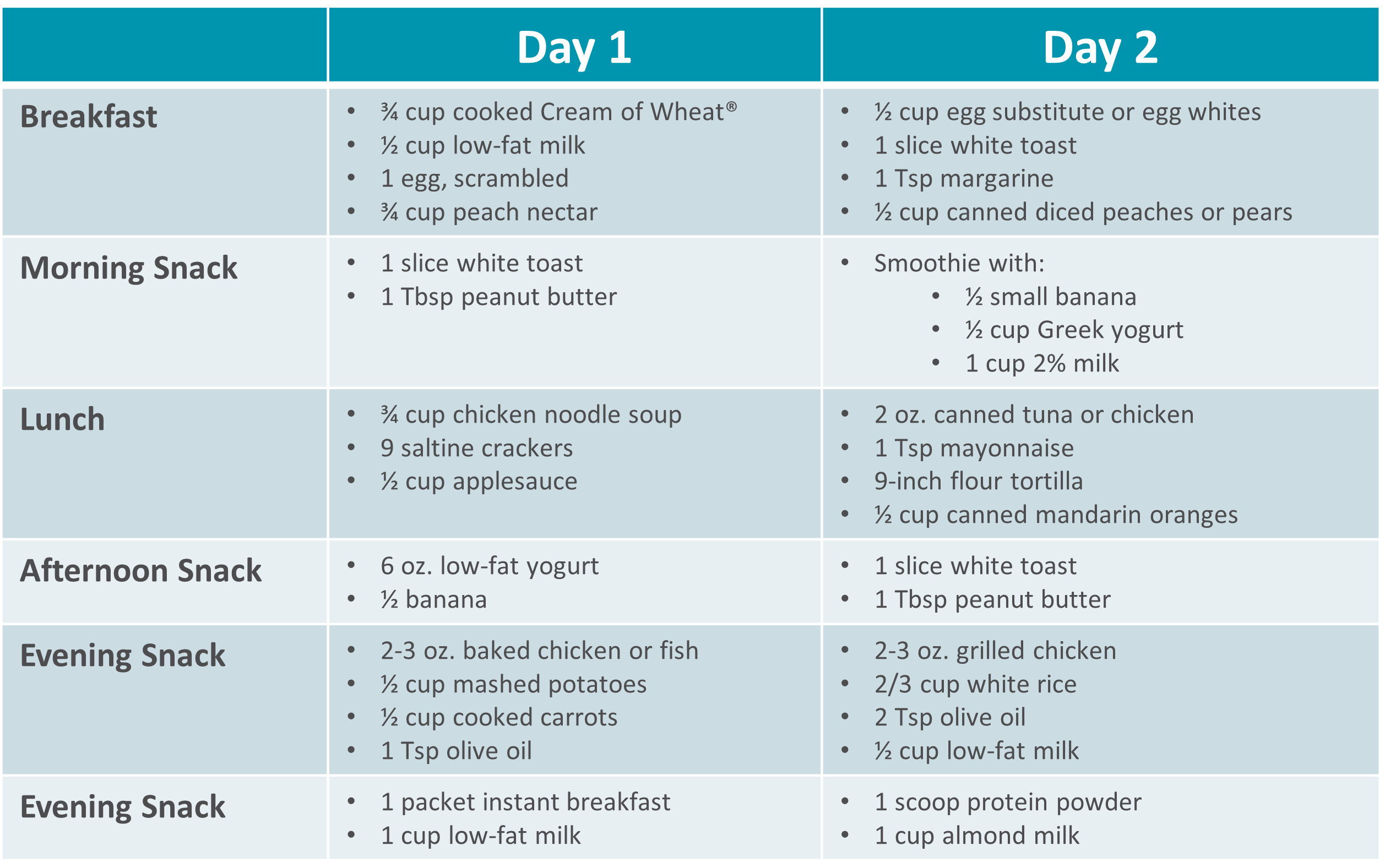 |
Please visit Restore+ to learn more about the nutrition support services offered by Option Care Health.
*This material is for informational purposes only. It does not replace the advice or counsel of a healthcare professional. Please consult with your Registered Dietitian for more detailed, individualized information.

sample menu
Short bowel syndrome (SBS), or intestinal failure, is a condition in which your body is unable to absorb enough nutrients from foods and fluids you consume. This can occur after a surgical resection or damage to your intestines. Symptoms and absorption vary by individual based on the amount and health of the remaining intestine. Symptoms of SBS can include diarrhea, dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities, and weight loss.
The following tips are intended to maximize absorption, improve your nutritional status and reduce dependence on parenteral nutrition.
- Mealtime
- Eat small, frequent meals (6-8 per day)
- Foods
- Eat protein at all meals: eggs, creamy peanut butter, chicken, fish, beef, tofu
- Choose complex carbohydrates such as bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes
- Limit raw vegetables to small amounts
- Avoid fruits with skin or edible seeds
- Limit raw fruits to very small portion twice a day
- Increase your soluble fiber to thicken output with foods such as bananas, applesauce, rice, oatmeal or use of soluble fiber supplements
- Avoid high fat foods such as fried foods if your colon is intact
- Use caution with dairy products – lactose intolerance is common with SBS
- Avoid concentrated sweets such as candy, desserts, and juice
- Avoid foods artificially sweetened with sorbitol or mannitol (Splenda® is okay)
- Fluids
- Drink isotonic fluids (with electrolytes), ideally oral rehydration solutions (see recipes below)
- Do not drink fluids with meals as it increases how quickly food passes through
- Limit to 4 oz. fluid during your meal to allow your food to be best absorbed
- Drink ½ hour before or 2 hours after eating
- If you do not have your colon, your fluid losses will be higher
- Otro
- If prescribed by your doctor, take antidiarrheal medication ½ hour before meals
- Salty foods such as pretzels or soups are usually well tolerated and help absorb fluid
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol
See below for help in choosing more optimal foods from each food group:
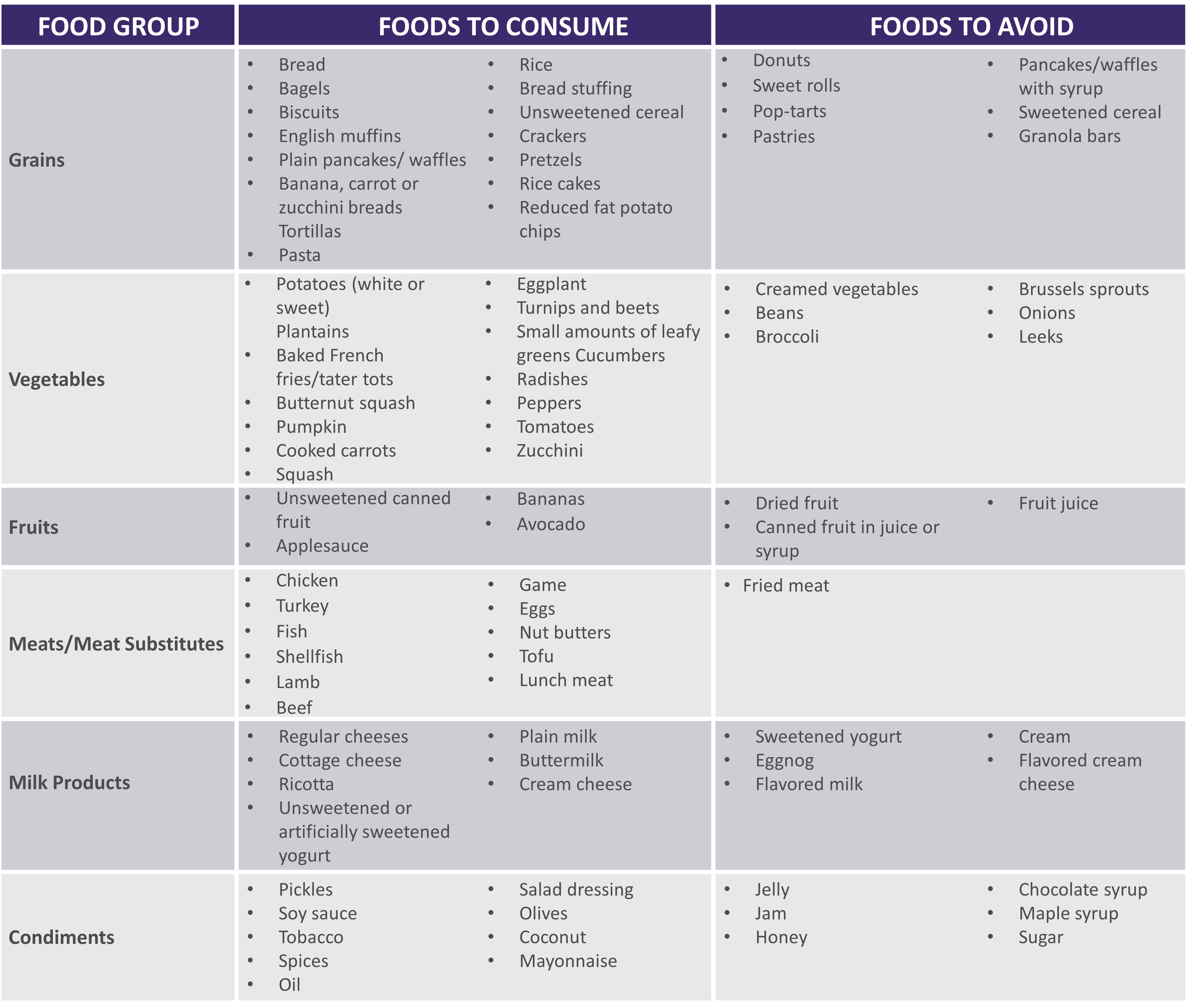 |
|
|
|
**For homemade ORS, discard after 24 hours if not consumed **Visit for more recipes: https://optioncarehealth.com/patients/resources/sbs-friendly-recipes |
SBS Sample Menu |
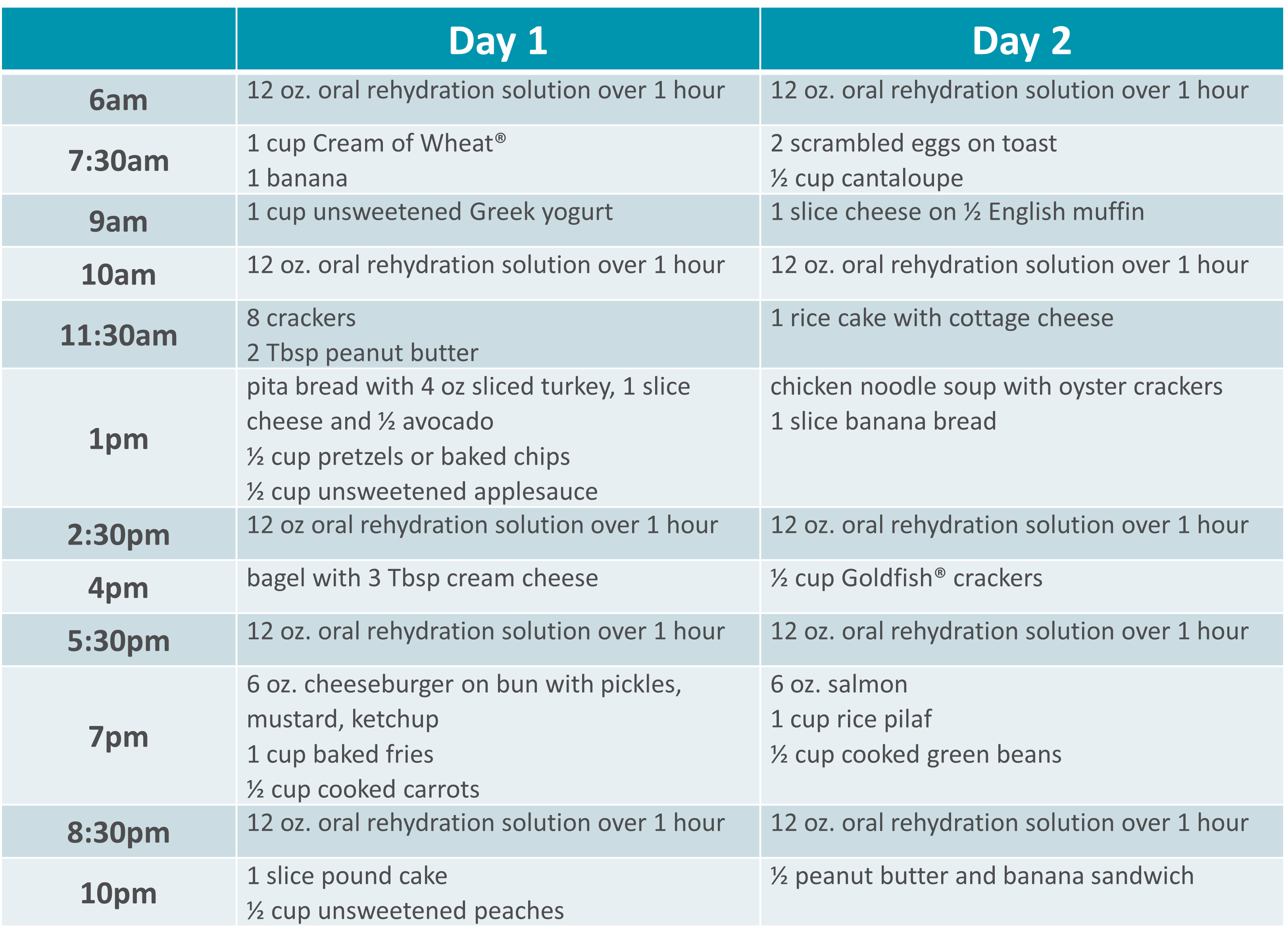 |
Please visit Restore+ to learn more about the nutrition support services offered by Option Care Health.
*This material is for informational purposes only. It does not replace the advice or counsel of a healthcare professional. Please consult with your Registered Dietitian for more detailed, individualized information.


